Sending Events
Send webhook events to your subscribers using the UI (for testing), API, or SDK (for production).
What are Events?
Events are occurrences in your application that you want to notify subscribers about. When you send an event, hookVM delivers it to all active subscriptions listening for that event type.
Event Flow:
- Your application sends an event
- hookVM receives and processes the event
- hookVM delivers to all matching subscriptions
- Subscribers receive the webhook
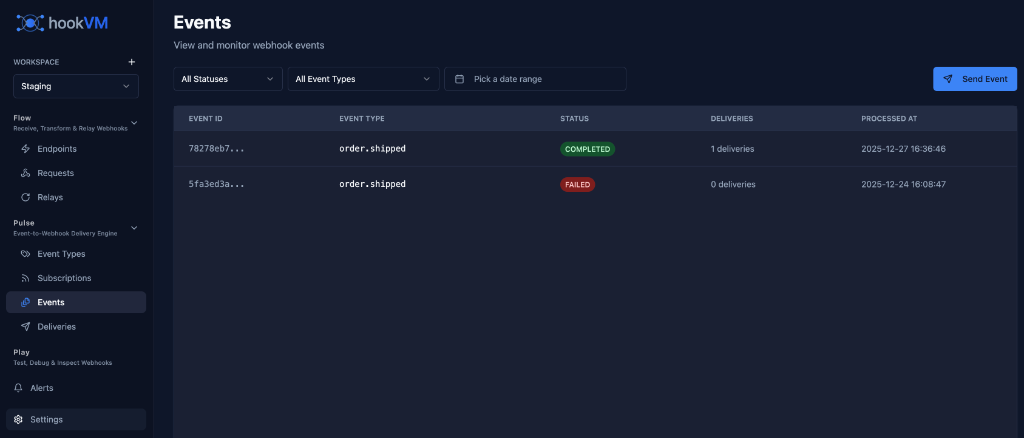
Events Page
View and monitor all sent events and their delivery status.
Key Features
Event Tracking: See all sent events
Status Monitoring: Track delivery success/failure
Filtering: Filter by status, event type, date
Delivery Count: See number of deliveries per event
Quick Send: Test events via UI
Event Columns
EVENT ID
Unique identifier for the event.
Format: Truncated ID (e.g., 78278cb7...)
Use Cases:
- Reference in API calls
- Track in logs
- Debug delivery issues
- Idempotency checks
EVENT TYPE
The type of event that was sent.
Examples:
order.shippeduser.createdpayment.completed
Use Case: Identify what kind of event occurred
STATUS
Delivery status of the event.
COMPLETED (Green badge):
- Successfully delivered to all subscriptions
- No errors
- All deliveries succeeded
FAILED (Red badge):
- Failed to deliver to one or more subscriptions
- After all retry attempts
- Requires investigation
PROCESSING (Yellow badge):
- Currently being delivered
- In progress
- Wait for completion
DELIVERIES
Number of delivery attempts made.
Format: {count} deliveries
Examples:
1 deliveries- Delivered to 1 subscription0 deliveries- No active subscriptions5 deliveries- Delivered to 5 subscriptions
Use Case: Track how many subscribers received the event
PROCESSED AT
Timestamp when the event was processed.
Format: YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
Example: 2025-12-27 16:36:46
Filtering Events
Use filters to find specific events quickly.
Filter by Status
Dropdown: "All Statuses"
Options:
- All Statuses
- Completed
- Failed
- Processing
Use Case: Focus on failed events for troubleshooting
Filter by Event Type
Dropdown: "All Event Types"
Options:
- All Event Types
- Specific event type (e.g.,
order.shipped)
Use Case: View events of a specific type
Filter by Date Range
Date Picker: "Pick a date range"
Select custom date range to view events.
Use Case: Investigate events during specific time period
Sending Events via UI (Testing)
Use the UI to send test events and verify your setup.
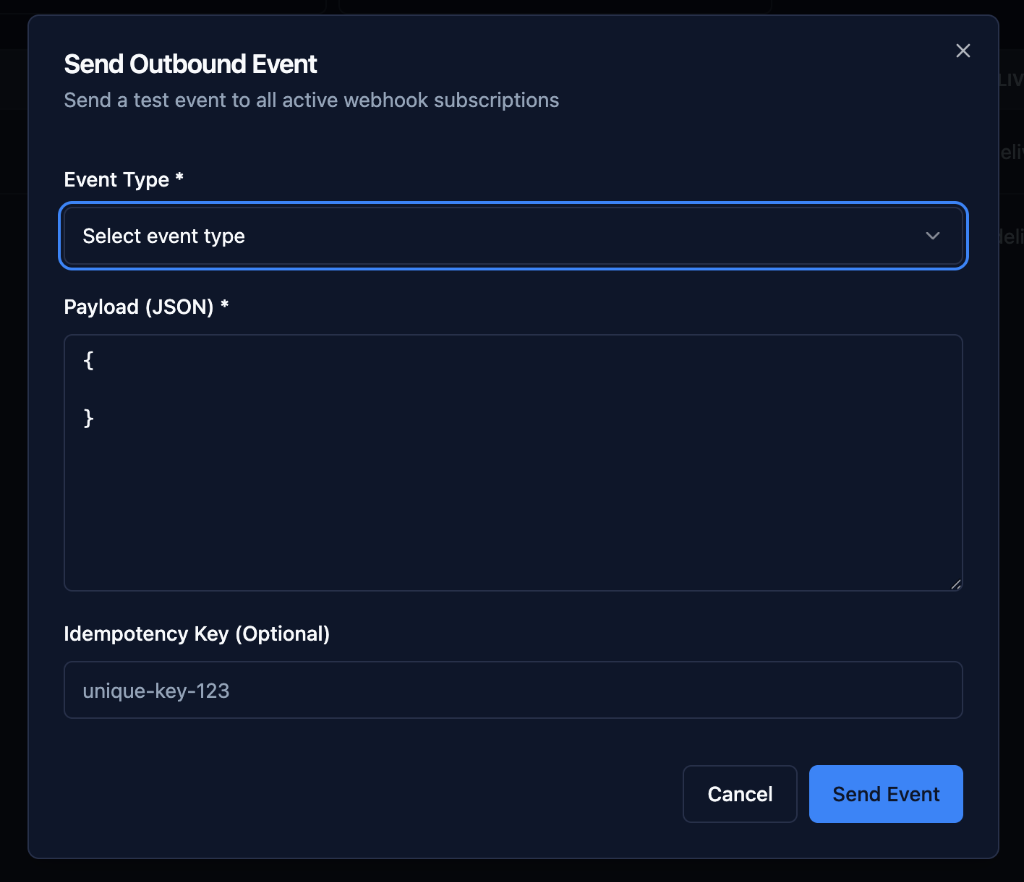
Step 1: Click Send Event
Click the "Send Event" button in the top right.
Step 2: Select Event Type
Event Type (Required):
- Select from dropdown
- Choose existing event type
- Example:
order.shipped
Step 3: Enter Payload
Payload (JSON) (Required):
Enter the event data in JSON format.
Example:
{
"order_id": "ord_12345",
"tracking_number": "TRK789",
"carrier": "UPS",
"shipped_at": "2025-12-27T10:00:00Z"
}
Requirements:
- Must be valid JSON
- Should match event type schema (if defined)
- Include all required fields
Step 4: Add Idempotency Key (Optional)
Idempotency Key (Optional):
Unique key to prevent duplicate event processing.
Example: unique-key-123
Use Cases:
- Prevent duplicate deliveries
- Retry safely
- Ensure exactly-once processing
Best Practice: Use a unique identifier from your system
order_id-shipped-timestamp
user_12345-created-20251227
payment_abc123-completed
Step 5: Send Event
Click "Send Event" to deliver to all active subscriptions.
What Happens:
- Event is validated
- Event is stored
- Matching subscriptions are found
- Deliveries are queued
- Webhooks are sent to subscribers
Sending Events via API (Production)
Send events programmatically using the hookVM API.
API Endpoint
POST /api/v1/events
Headers
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Request Body
{
"event_type": "order.shipped",
"data": {
"order_id": "ord_12345",
"tracking_number": "TRK789",
"carrier": "UPS",
"shipped_at": "2025-12-27T10:00:00Z"
},
"idempotency_key": "ord_12345-shipped-20251227"
}
Response
Success (200 OK):
{
"event_id": "evt_abc123def456",
"event_type": "order.shipped",
"status": "processing",
"deliveries_queued": 3,
"created_at": "2025-12-27T10:00:00Z"
}
Error (400 Bad Request):
{
"error": "validation_error",
"message": "Invalid JSON payload",
"details": {
"field": "data.shipped_at",
"error": "Invalid date format"
}
}
cURL Example
curl -X POST https://api.hookvm.com/v1/events \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your-api-key" \
-d '{
"event_type": "order.shipped",
"data": {
"order_id": "ord_12345",
"tracking_number": "TRK789",
"carrier": "UPS",
"shipped_at": "2025-12-27T10:00:00Z"
},
"idempotency_key": "ord_12345-shipped-20251227"
}'
Sending Events via SDK (Recommended)
Use hookVM SDKs for easier integration and better developer experience.
Node.js
Installation:
npm install @hookvm/node
Usage:
const hookvm = require('@hookvm/node');
const client = new hookvm.Client('your-api-key');
// Send event
const event = await client.events.send({
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: {
order_id: 'ord_12345',
tracking_number: 'TRK789',
carrier: 'UPS',
shipped_at: new Date().toISOString()
},
idempotencyKey: 'ord_12345-shipped-20251227'
});
console.log('Event sent:', event.id);
console.log('Deliveries queued:', event.deliveries_queued);
Batch Sending:
// Send multiple events efficiently
const events = await client.events.sendBatch([
{
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: { order_id: 'ord_1', tracking_number: 'TRK1' }
},
{
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: { order_id: 'ord_2', tracking_number: 'TRK2' }
},
{
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: { order_id: 'ord_3', tracking_number: 'TRK3' }
}
]);
console.log(`Sent ${events.length} events`);
Python
Installation:
pip install hookvm
Usage:
import hookvm
from datetime import datetime
client = hookvm.Client('your-api-key')
# Send event
event = client.events.send(
event_type='order.shipped',
data={
'order_id': 'ord_12345',
'tracking_number': 'TRK789',
'carrier': 'UPS',
'shipped_at': datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
},
idempotency_key='ord_12345-shipped-20251227'
)
print(f'Event sent: {event.id}')
print(f'Deliveries queued: {event.deliveries_queued}')
Batch Sending:
# Send multiple events
events = client.events.send_batch([
{
'event_type': 'order.shipped',
'data': {'order_id': 'ord_1', 'tracking_number': 'TRK1'}
},
{
'event_type': 'order.shipped',
'data': {'order_id': 'ord_2', 'tracking_number': 'TRK2'}
}
])
print(f'Sent {len(events)} events')
Go
Installation:
go get github.com/hookvm/hookvm-go
Usage:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/hookvm/hookvm-go"
)
func main() {
client := hookvm.NewClient("your-api-key")
// Send event
event, err := client.Events.Send(&hookvm.EventSendParams{
EventType: "order.shipped",
Data: map[string]interface{}{
"order_id": "ord_12345",
"tracking_number": "TRK789",
"carrier": "UPS",
"shipped_at": time.Now().Format(time.RFC3339),
},
IdempotencyKey: "ord_12345-shipped-20251227",
})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Event sent: %s\n", event.ID)
fmt.Printf("Deliveries queued: %d\n", event.DeliveriesQueued)
}
Idempotency
Prevent duplicate event processing using idempotency keys.
What is Idempotency?
Idempotency ensures that sending the same event multiple times has the same effect as sending it once.
Use Cases:
- Network retries
- Application crashes
- Duplicate requests
- Ensuring exactly-once delivery
How It Works
- First Request: Event is processed and delivered
- Duplicate Request: Same idempotency key detected
- Response: Returns original event, no new deliveries
Idempotency Key Format
Best Practices:
{resource_id}-{action}-{timestamp}
{resource_id}-{action}-{unique_id}
{uuid}
Examples:
order_12345-shipped-20251227
user_abc123-created-1640000000
payment_xyz789-completed
550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000
Example with Idempotency
// First request
const event1 = await client.events.send({
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: { order_id: 'ord_123' },
idempotencyKey: 'ord_123-shipped-20251227'
});
// Result: Event sent, 3 deliveries queued
// Duplicate request (network retry)
const event2 = await client.events.send({
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: { order_id: 'ord_123' },
idempotencyKey: 'ord_123-shipped-20251227'
});
// Result: Returns same event, no new deliveries
console.log(event1.id === event2.id); // true
Event Payload Best Practices
Include Timestamps
Always include event timestamp:
{
"event_type": "order.shipped",
"data": {
"order_id": "ord_123",
"shipped_at": "2025-12-27T10:00:00Z",
"processed_at": "2025-12-27T10:00:01Z"
}
}
Include Resource IDs
Make it easy to identify resources:
{
"event_type": "payment.completed",
"data": {
"payment_id": "pay_123",
"order_id": "ord_456",
"customer_id": "cust_789",
"amount": 99.99,
"currency": "USD"
}
}
Use Consistent Structure
Maintain consistent payload structure:
{
"event_id": "evt_abc123",
"event_type": "user.created",
"occurred_at": "2025-12-27T10:00:00Z",
"data": {
"user_id": "user_123",
"email": "user@example.com",
"plan": "pro"
},
"metadata": {
"source": "web_app",
"version": "v1"
}
}
Avoid Sensitive Data
Don't include sensitive information:
{
"event_type": "user.created",
"data": {
"user_id": "user_123",
"email": "user@example.com",
// ❌ Don't include:
// "password": "...",
// "credit_card": "...",
// "ssn": "..."
}
}
Common Integration Patterns
E-commerce Order Events
// When order is shipped
async function onOrderShipped(order) {
await hookvm.events.send({
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: {
order_id: order.id,
customer_id: order.customer_id,
tracking_number: order.tracking_number,
carrier: order.carrier,
shipped_at: new Date().toISOString(),
items: order.items.map(item => ({
product_id: item.product_id,
quantity: item.quantity
}))
},
idempotencyKey: `${order.id}-shipped-${Date.now()}`
});
}
User Lifecycle Events
// When user signs up
async function onUserSignup(user) {
await hookvm.events.send({
eventType: 'user.created',
data: {
user_id: user.id,
email: user.email,
plan: user.plan,
created_at: user.created_at
},
idempotencyKey: `${user.id}-created`
});
}
// When user upgrades
async function onUserUpgrade(user, newPlan) {
await hookvm.events.send({
eventType: 'subscription.upgraded',
data: {
user_id: user.id,
old_plan: user.plan,
new_plan: newPlan,
upgraded_at: new Date().toISOString()
},
idempotencyKey: `${user.id}-upgraded-${Date.now()}`
});
}
Payment Events
// When payment succeeds
async function onPaymentSuccess(payment) {
await hookvm.events.send({
eventType: 'payment.completed',
data: {
payment_id: payment.id,
order_id: payment.order_id,
amount: payment.amount,
currency: payment.currency,
payment_method: payment.method,
completed_at: new Date().toISOString()
},
idempotencyKey: `${payment.id}-completed`
});
}
Error Handling
Handle API Errors
try {
const event = await client.events.send({
eventType: 'order.shipped',
data: { order_id: 'ord_123' }
});
console.log('Event sent successfully:', event.id);
} catch (error) {
if (error.code === 'validation_error') {
console.error('Invalid payload:', error.message);
// Fix payload and retry
} else if (error.code === 'rate_limit_exceeded') {
console.error('Rate limit exceeded, retry later');
// Implement backoff and retry
} else if (error.code === 'authentication_error') {
console.error('Invalid API key');
// Check API key configuration
} else {
console.error('Unexpected error:', error);
// Log and alert
}
}
Implement Retries
async function sendEventWithRetry(eventData, maxRetries = 3) {
for (let attempt = 1; attempt <= maxRetries; attempt++) {
try {
return await client.events.send(eventData);
} catch (error) {
if (attempt === maxRetries) {
throw error; // Final attempt failed
}
// Exponential backoff
const delay = Math.pow(2, attempt) * 1000;
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
}
}
}
Best Practices
Event Sending
✅ Use Idempotency Keys: Prevent duplicates
✅ Include Timestamps: Track when events occurred
✅ Use SDK: Easier than raw API calls
✅ Handle Errors: Implement proper error handling
Performance
✅ Batch Events: Send multiple events together
✅ Async Processing: Don't block user requests
✅ Queue Events: Use message queue for reliability
✅ Monitor Volume: Track event sending rates
Security
✅ Protect API Keys: Store securely
✅ Validate Payloads: Check data before sending
✅ Avoid Sensitive Data: Don't send passwords, tokens
✅ Use HTTPS: Always use secure connections
Monitoring
✅ Track Success Rates: Monitor delivery success
✅ Alert on Failures: Set up failure alerts
✅ Log Events: Keep audit trail
✅ Review Regularly: Check event patterns
Troubleshooting
Event Not Sent
Possible Causes:
- Invalid API key
- Invalid event type
- Invalid JSON payload
- Rate limit exceeded
Solutions:
- Verify API key is correct
- Check event type exists
- Validate JSON syntax
- Check rate limits
No Deliveries
Possible Causes:
- No active subscriptions
- All subscriptions disabled
- Event type mismatch
Solutions:
- Create subscriptions
- Enable subscriptions
- Verify event type matches
Duplicate Events
Possible Causes:
- No idempotency key
- Different idempotency keys
- Application retry logic
Solutions:
- Always use idempotency keys
- Use consistent key format
- Check application retry logic
Next Steps
- Monitoring Deliveries - Track delivery status
- Event Types - Manage event types
- Subscriptions - Manage subscriptions
Ready to notify subscribers? Start sending events to your customers! 🚀